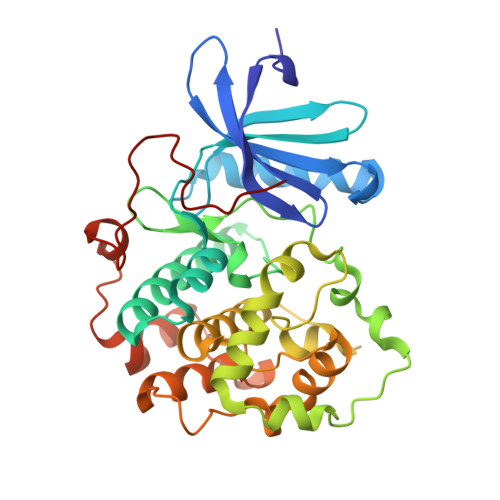
Structural Basis for Auto-Inhibition of the NDR1 Kinase Domain by an Atypically Long Activation Segment.
Xiong, S., Lorenzen, K., Couzens, A.L., Templeton, C.M., Rajendran, D., Mao, D.Y.L., Juang, Y.C., Chiovitti, D., Kurinov, I., Guettler, S., Gingras, A.C., Sicheri, F.(2018) Structure 26: 1101-1115.e6
- PubMed: 29983373
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2018.05.014
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BXI - PubMed Abstract:
The human NDR family kinases control diverse aspects of cell growth, and are regulated through phosphorylation and association with scaffolds such as MOB1. Here, we report the crystal structure of the human NDR1 kinase domain in its non-phosphorylated state, revealing a fully resolved atypically long activation segment that blocks substrate binding and stabilizes a non-productive position of helix αC. Consistent with an auto-inhibitory function, mutations within the activation segment of NDR1 dramatically enhance in vitro kinase activity. Interestingly, NDR1 catalytic activity is further potentiated by MOB1 binding, suggesting that regulation through modulation of the activation segment and by MOB1 binding are mechanistically distinct. Lastly, deleting the auto-inhibitory activation segment of NDR1 causes a marked increase in the association with upstream Hippo pathway components and the Furry scaffold. These findings provide a point of departure for future efforts to explore the cellular functions and the mechanism of NDR1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute, Sinai Health System, 600 University Avenue, Toronto, ON M5G 1X5, Canada; Department of Biochemistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON M5S 1A8, Canada.